Interoperability in healthcare generates a literature of systems, devices, or applications. It is capable of guaranteed seamless and secure exchange. Moreover, the interpretation of data is notwithstanding their gender, location, or institutional character. Similarly, the information has a flow that permits data sharing among different platforms, a required attribute for industries.
It includes the health, finance, and technologies in improving functions in the areas of research and development and enhancing user experiences. It results in a lower data silo, compliance with industry standards, and wider operational efficiency. This step leads to an elevation of both service quality and innovation. Read on to learn more interesting information!
What Is Interoperability in Healthcare?
To understand interoperability in healthcare, consider your workflow. You have an HMS on one end, which your personnel utilize to gather, organize, and process data from different departments and EHRs that your patients cannot access on the other end. In between, there is a parceling and claims management system that works independently.
Moreover, if all these systems are integrated, then they function as one cohesive system where health information is exchanged freely. They can share and receive information amongst themselves and with other similar systems outside of your organization without obstruction. By contrast, data interoperability in healthcare information systems assures seamless integration of data. It can be deployed at a regional or even countrywide scope to increase the service quality rendered, and your clinic can save millions in the process.
Still waiting for some virtual assistance to handle your practice as you want to focus on patient care? If so, no need to worry at all! You may contact us at MAVA Care. We are here to assist and tackle your administrative workflow!
Interoperability Solutions in Healthcare
Interoperability in healthcare brings together different medical systems, hospitals, and clinics by allowing patient information to be shared easily. These solutions electronically link EHRs to lab results, prescriptions, and imaging studies so that nurses and doctors can access the whole patient record at the point of care.
Furthermore, EHR interoperability helps providers to communicate better because when different systems ‘speak the same language,’ misunderstandings are reduced, errors are minimized, and patient safety is increased. Therefore, with interoperability, patients can be treated better and faster because all their caregivers have access to the patient information. It also supports telehealth because doctors can review patients’ charts during virtual visits.
However, interoperability reduces time spent on clinical documentation and duplicate diagnostic testing, which reduces the cost of patient care. The more clinics and hospitals adopt these solutions the more integrated, secure, and responsive the healthcare system will be to the patient’s needs.
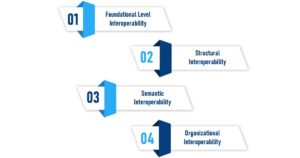
Types of Interoperability in Healthcare
Multiple systems can complete all components of care, thus saving valuable time and resources. Multiple systems can complete all components of care, thus saving valuable time and resources.
1. Foundational Level Interoperability
Foundational level interoperability is the lowest tier on the scale. It enables direct bi-directional data interoperability in healthcare between two health systems. Interoperability begins with this foundation, but systems at this level cannot exchange operative data. For instance, HIMSS, one of the prominent names in healthcare transformation, identified these levels as foundational, structural, semantic, and organizational.
2. Structural Interoperability
The exchange of information is at the core of structural interoperability. At this level, systems are now able to examine in detail what exactly gets sent between them. Imagine a pharmacy system where medication lists can be processed with the same information exchange format as the provider system.
3. Semantic Interoperability
Two or more parties agree that the actual meaning and application of data interoperability in healthcare is semantic interoperability. Systems that operate under semantic interoperability in healthcare are capable of receiving units of work to be performed in a broken down and shared manner. For instance, it is now possible for systems to recognize a vocabulary, medication shorthand, and other distinguishing features that are exchanged without manual input.
4. Organizational Interoperability
Organizational interoperability concerns what resources are needed, so your clinic’s semantic interoperability can become a working system. This level includes details of the implementation or managerial processes and even legal procedures required to make the idea a reality.
Examples of Semantic Data Interoperability in Healthcare
How can to improve interoperability in healthcare? Let’s find out! To enhance interoperability in healthcare, there needs to be the use of standards like HL7 and FHIR and oding systems like SNOMED CT and LOINC to guarantee systems integration.
In addition, the term ‘semantic interoperability’ in healthcare encompasses the capacity to deal with the barriers to interoperability in healthcare. For instance, if one hospital’s EHR (electronic health record) is sent to another, it needs to be factored in that the other hospital has access to medication details, lab results, and diagnoses, which all should be coded in standard formats whether it is SNOMED CT or LOINC.
Thus, it enables both systems to comprehend the information provided accurately and minimizes the need for manual adjustments, which increases errors and improves the coordination of care. Another example would be the fusion of clinical decision support systems (CDS) and EHRs. The CDS can determine a patient’s history, allergies, and labs when a physician issues a prescription and does so with set terms.
Importance of Interoperability in Healthcare
Let us consider the significance of interoperability within healthcare:
- Enables coordination of care between different providers to achieve better results.
- Reduces test and medication errors along with redundancy.
- Creates efficiencies in information transfer for remote monitoring of patients.
- Facilitates epidemiologic surveillance and population health management.
- Avoids duplicative testing and misallocation of resources.
- Customarily tracks compliance with HIPAA and other requirements governing healthcare.
- Permits people to control their health records with ease.
Benefits Of Interoperability in Healthcare
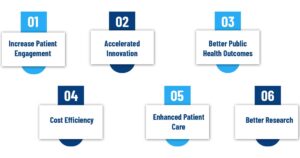
1. Increase Patient Engagement
Interoperability allows patients to access their medical records, lab results, and treatment history through digital platforms like patient portals and mobile apps. This transparency encourages individuals to take an active role in managing their health, scheduling appointments, and following treatment plans when patients have easy access to their health information.
2. Accelerated Innovation
The cooperative exchange of information allows healthcare providers to collaborate with technology developers to build efficient medical solutions. Healthcare interoperability enables the sharing of data in seeing AI, individualized treatment plans, and even real-time health monitoring. Similarly, new technologies in medicine and new ways of providing treatment. So, new medicine-oriented telecommunication services have become prevalent, advancing data interoperability in healthcare services.
3. Better Public Health Outcomes
Interoperability increases public health initiatives by offering near real-time information on disease outbreaks, vaccination, and chronic conditions. Healthcare organizations and government agencies can follow up on trends, manage emergencies, and apply preventive measures more readily. Interoperability increases the efficiency of data collection and analysis, which improves community health and readiness.
4. Cost Efficiency
The healthcare systems considerably reduce income-generating tests and procedures, superfluous hospital visits, and repetitive diagnostics. Multiple systems can complete all components of care, thus saving valuable time and resources. Such reasoning brings forth the notion that superlative care is attainable and affordable for a patient’s financial constraints.
5. Enhanced Patient Care
Ensures the holistic circulation of information which provides a patient diagnosis and treatment as needed. The healthcare providers can easily access relevant information for the patient. Interoperability fosters collaboration between primary care physicians, specialists, and hospitals, which strengthens continuity of care. Hence, patient safety and medication error reduction are improved along with emergency response time.
6. Better Research
It improves the capacity of researchers to combine information from different instruments and sources to strengthen the credibility and generalizability of the research study. This flexibility in the use of actual patient data improves clinical trials and facilitates medicine development. It improves strategies for disease prevention which beneficially affects the health industry. Furthermore, interoperability has a positive impact on collaboration between research institutions, hospitals, and pharmaceutical companies.
Final Thoughts
Interoperability in healthcare provides clinical quality and reduces errors and redundancy in care. Interoperability is the ability to communicate and exchange data among vendors, which means clinicians have access to complete, accurate, and up-to-date information.
This tremendously facilitates better diagnosis, treatment planning, and clinical decision-making. Interoperability includes applicable contributions to public health initiatives. Thus, it is all gathered through research and analytics through data aggregation. The breaking down of data locations leads to a reduction in duplicative testing and low-cost coordination in workflows. For more information and details, reach out to us at MACA Care.
FAQ’s
What is meant by an example of data interoperability?
An example of data interoperability is when a patient’s electronic health record from one hospital can be transmitted to another facility in standard formats such as HL7 or FHIR.
What is the interoperability role in health care?
In healthcare, interoperability incorporates the defining factors for different exchange protocols for information, its integration using these standardized protocols, and the correct meanings of the data across the healthcare delivery system for a continuum of care.
Which are the three types of interoperability?
Interoperability may refer to foundational (the basic data exchange), structural (data formatting and organization), and semantic interoperation.
What is interoperability in data analysis?
Interoperability in data analysis means that the ability of the systems to exchange, process, and interpret data correctly will lead to meaningful insights and decision-making.









