A pharmacy medical billing and coding entails handling medications and getting payment from the insurer. The adjudication process begins with checking eligibility and verifying the prescriptions. Medical coders using Medicaid billing software apply appropriate HCPCS or NDC codes to the medications. After this, billers submit claims to the relevant insurer or PBM for adjudication.
Similarly, denied claims are adjusted or appealed. Payments are processed; debts, if there are any, are collected. HIPAA and other insurance guideline policies have to be adhered to along all the phases. Here in this article, we’ll explain the pharmacy medical billing services, its process, and its challenges. Stay with us till the end and collect the useful information!
What Is Pharmacy Billing?
Pharmacy billing is the process of managing and submitting claims for reimbursement about the expenditures on medicines and pharmacy services to third parties like an insurance company. The system is organized in a manner that a patient receives the medicines while their pharmacy gets reimbursed appropriately.
Furthermore, pharmacy billing services also include verifying the patient’s insurance eligibility, filing the prescription, estimating the total, and applying any other payments. It also includes discounts or co-pays and finalizing the claims through the relevant software or system. It is also the responsibility of pharmacy personnel to deal with claim denials and other such issues so that payments are made with minimal disruptions.
However, poor pharmacy medical billing can lead to disaster in the running of the pharmacy business and deny patients essential pharmaceutical products. Attention to detail, knowledge and compliance with laws and regulations, and an understanding of the claim. To avail of the smooth and error-free billing and coding services, you may contact us at MAVA Care.
Pharmacy Billing and Reimbursement
Pharmacy medical billing requires claims for prescription medications to be submitted to insurance companies. The process also involves verifying eligibility for paying patients, application of an appropriate National Drug Code (NDC), along compliance with payer-specific guidelines.
In addition, to avoid claim denials and to obtain the maximum payment for medicines dispensed, pharmacies must abide by rules set by Medicare and Medicaid and private insurers. In pharmacy billing, reimbursement will depend on such things as formulary coverage, and whether a prior authorization is selective.
Hence, it prefers a medicine list/pricing strategy in effect and the rate at which payment has been negotiated. To remain financially sound while enabling patients to receive needed medications without unnecessary delay, pharmacists must handle claim rejections.
Pharmacy Billing Process
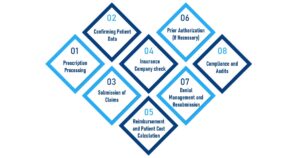
1. Prescription Processing
The healthcare provider prescribes the patient’s prescription. They can either pass it on through electronic means or in print form on paper. When a pharmacy receives prescriptions, it checks them for accuracy and legibility. The pharmacy confirms that the medicine is in stock. The prescriber sorts out all discrepancies before the pharmacy proceeds further.
2. Confirming Patient Data
The pharmacy verifies the patient’s demographics and insurance details. This covers checking eligibility, coverage, and plan-specific requirements. For a patient with multiple insurance plans, coordination of benefits (COB) is performed. Resolve each dispute or absent information before the claim goes through.
3. Submission of Claims
Through an operator of Pharmacy Benefit Manager (PBM), the pharmacy gives the claim to the patient’s insurance company electronically. Patient information, medicine details, dosage, prescriber information, and expenses are all part of a claim. Real-time submission is the normal method for the insurance company to glance at and decide immediately on whether they are going to pay this claim or reject the whole thing. Any errors in sub-mission can lead to denials or rejections.
4. Insurance Company check
The insurance company or PBM re-evaluates the claim according to their rules. They check whether the participants are eligible, whether their beds are in the formulary status, and if they receive any fringe benefits. If the claim meets all necessary conditions, then the company approves it. If problems arise during processing or submission, the company rejects the claim with an explicit denial code.
5. Reimbursement and Patient Cost Calculation
The pharmacy will inform patients about their specific cash obligation in advance (e.g., co-payment or deductible). If the claim is not honored and denied, the patients themselves might have to pay the whole price out of pocket or find other remedies. Moreover, accurate payment tallying by the pharmacy is crucial for maintaining its financial records. Correct cost calculation prevents overcharging while creating an open financial picture.
6. Prior Authorization (If Necessary)
Some medicines require prior authorization before they will be given coverage. The pharmacy contacts the provider to provide them with the necessary documentation in support of their request. The insurance reviews the application and either accepts it or turns it down. If it is denied, the provider may appeal with more supporting documents like x-rays and medical reports. This step prevents needless refusals and ensures necessary medications go out to patients.
7. Denial Management and Resubmission
The team implements the necessary modifications, and the pharmacy resubmits the claim to the insurer. The pharmacy may elevate the denial through an appeals process if the denial persists. Interacting with the insurer and provider guarantees pharmacy billing solutions. Proficient denial administration boosts claim approval rates and diminishes lost revenue.
8. Compliance and Audits
Pharmacies must legally comply with HIPAA and CMS and the stipulations of particular insurance providers. Also, they document claims and prescriptions to the level required for auditing. Routine audits reveal gaps within compliance, mark discrepancies, and identify fraud risks. In the event of non-compliance, penalties and negative reimbursement will occur. Therefore, an accurate record will facilitate and smoothen the audit process.
Outsource Pharmacy Billing Services from A Reliable Medical Billing Company
It’s a complex operation to go about Pharmacy medical billing. It can involve precise coding, timely claim submissions, and constant keeping up with new rules and regulations. You can streamline the management of the revenue cycle, eliminate errors, and achieve maximum reimbursements by using pharmacy billing services.
By contrast, with a reliable pharmacy billing company providing accurate prescription claims and insurance verification as well as timely follow-up on accounts receivable, pharmacies can concentrate on patient care without financial setbacks.
At MAVA Care, we specialize in pharmacy medical billing services tailor-made to suit your requirements. Our professional team can help with seamless claim processing, compliance adherence, and timely reimbursements so that your practice remains financially viable. You can rely on MAVA Care to provide accurate medical billing services. Contact us today, and get on track with your pharmacy medical billing!
Challenges in Pharmacy Medical Billing

1. Complex Reimbursement Processes
Pharmacy medical billing encompasses several reimbursement approaches like claims, co-payments, and even pay-per-billing from other health insurance companies. Claim denials or payment delays may occur as a result of inappropriate coding or lack of adequate documentation. Pharmacies, moreover, have to comply with different insurer-specific billing rules, which complicates matters.
2. Insurance Verification and Prior Authorization
Pharmacies must obtain insurance verification and prior approval for select medications before processing any prescription. Either a pharmacy or an insurance company can cause that gap. Also, they can further postpone getting medication. However, users can enhance efficiency and precision.
3. Changing Regulations and Compliance
Changes in pharmacy billing codes (ICD 10, CPT, and HCPCS) are frequent, and pharmacies may need to adopt new processes to remain compliant, which is a moving target. Non-compliance with HIPAA, CMS, or insurance policies can result in audits or claim denials and impose legal and financial penalties. Staying on top of changing policies and rules comes at a cost in terms of infrastructure investment.
4. Denial Management and Claim Rejections
Improper coding, information omission, and erroneous claim duplications are some of the many reasons for claim denials, and these can greatly impact reimbursement cash flow. To aid in recovering these lost reimbursements, we must implement a systematic approach to resubmit appeals.
5. Coordination of Benefits (COB) Issues
Patients possessing multiple forms of insurance coverage necessitate precise alignment from the primary and secondary insurers. Errors in COB outcomes include claim underpayment, rejection, or disputes, which bring heavy financial strain to both the patients and the pharmacies. Establishing the correct payer liability determines hassle-free claim processing. Effective handling of coordinating benefits prevents superfluous loss of revenue as well as dissatisfaction from the patients.
Bottom Lines
Managing Pharmacy medical billing is key to reimbursement, capital, and operational activities in the healthcare sphere. Managing billing entails filing claims, verifying whether an insurance payer will reimburse the expense, and collecting patient co-payments. All of these steps must be executed meticulously to maximize any income opportunities.
Moreover, completing billing tasks accurately eliminates mistakes, many of which consume extensive time from claims being paid and instead seeing delays. In this regard, billing reduces the direct expenses for patients while increasing their access to necessary medications. Improper substantiation and coding can result in legal and financial exposure. MAVA Care offers precise billing services that promote revenue optimization and compliance, which most pharmacies need.
FAQs
What is pharmacy medical billing?
Pharmacy medical billing is the process of billing the insurance company for medicines, clinical services, and pharmaceutical care services. It assures pharmacies will be paid for prescription medications, counseling, educating patients and administering vaccines. Billing requires adherence to the health insurance company’s policies, coding structure, and laws. They ensure that there is adequate documentation and submission of claims orders to avoid payment denial and delays.
How to do billing in a pharmacy?
Pharmacy billing begins with validating the patient’s insurance and the details of their prescription coverage. Medications are billed using National Drug Codes (NDC), and medical services through CPT or HCPCS codes.
What CPT codes can pharmacists bill?
Pharmacists can bill for services like medication therapy management (MTM) using 99605, 99606, and 99607. Immunization services receive codes 90471-90474 based on the type of administration. Point-of-care testing and counseling services may have codes such as 99211 for evaluation and management services for uncomplicated problems.
Do pharmacy techs do medical billing?
Pharmacy technicians help with medical billing; however, they are not allowed to submit claims on their own. Claim processing, verification, and prior authorization work is done under the supervision of a pharmacist. Claim accuracy is completed, along with claims denial and reimbursement processes. Their role is to help pharmacists with the billing system and claims for insurance in an orderly manner.








